Device Allocation Manager
A device is either a physical peripheral that is connected to a computer
or a software-simulated device called a pseudo-device. Because devices provide a means
for the import and export of data to and from a system, devices
must be controlled to properly protect the data. Trusted Extensions uses device allocation
and device label ranges to control data flowing through devices.
Examples of devices that have label ranges are frame buffers, tape drives, diskette
and CD-ROM drives, printers, and USB devices.
Users allocate devices through the Device Allocation Manager. The Device Allocation Manager mounts
the device, runs a clean script to prepare the device, and performs the
allocation. When finished, the user deallocates the device through the Device Allocation Manager,
which runs another clean script, and unmounts and deallocates the device.
Figure 8-1 Device Allocation Manager Icon in Trusted CDE
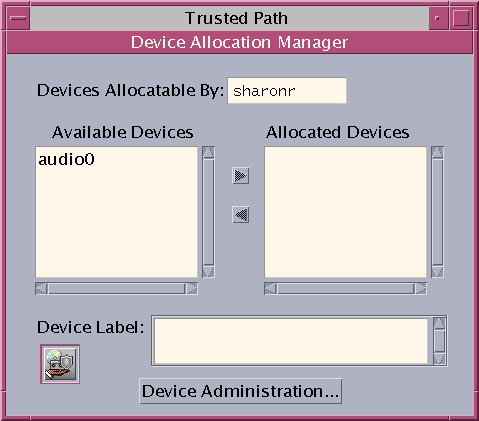
You can manage devices by using the Device Administration tool from the Device
Allocation Manager. Regular users cannot access the Device Administration tool.
Note - In Solaris Trusted Extensions (JDS), this GUI is named Device Manager, and
the Device Administration button is named Administration.
Figure 8-2 Device Allocation Manager GUI
For more information about device protection in Trusted Extensions, see Chapter 23, Managing Devices for Trusted Extensions (Tasks).